How Emotions Work: A Guide to Navigating Your Inner World
If you’re here, it’s likely because you’re curious about emotions—how they work, why they sometimes feel overwhelming, and how therapy can help you better understand and manage them. As a therapist, I often work with clients who struggle to make sense of their emotions, or who feel “stuck” in emotional patterns that seem to take over.
In this post, we’ll explore the science and psychology behind emotions, why they’re so important to our well-being, and how gaining a deeper understanding of them can lead to greater emotional balance and mental health.
What Are Emotions, Exactly?
At their core, emotions are physiological responses to experiences, thoughts, and situations. They’re a mix of physical sensations, mental interpretations, and behavioral reactions that help us process and respond to the world around us. While emotions can feel overwhelming at times, they’re actually vital for our survival and mental health—they provide us with valuable information about our needs, desires, and boundaries.
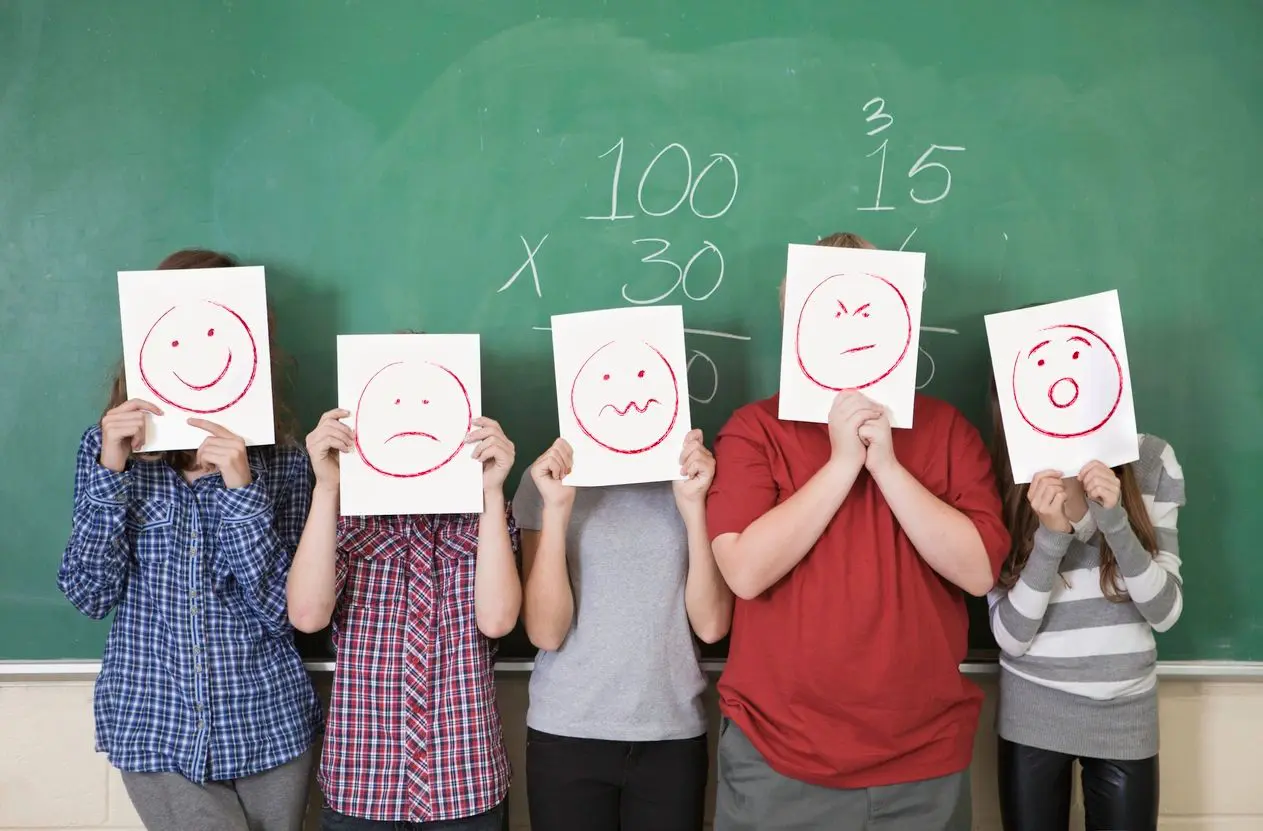
Emotions are often categorized into basic feelings like:
- Happiness
- Sadness
- Anger
- Fear
- Surprise
- Disgust
However, we experience many variations of these core emotions (e.g., frustration, joy, shame, anxiety), which can be triggered by both internal and external events.
The Science Behind Emotions: The Brain and Body Connection
Emotions are a result of complex interactions between our brain, nervous system, and body. When we experience something emotional, our brain processes the event and sends signals throughout our body to prepare us for a reaction. This could be a physical change (like an increased heart rate when we’re anxious or an endorphin rush when we’re happy), or a mental shift (like feeling a sense of dread or excitement).
Here’s a basic breakdown of how this works:
- The Limbic System: This part of the brain, often called the “emotional brain,” plays a key role in processing emotions. The amygdala, in particular, is responsible for detecting threats and triggering the fight-or-flight response. It also helps process emotional memories and reactions.
- The Prefrontal Cortex: This area of the brain helps us regulate our emotions and make sense of them. It allows us to think through our emotional experiences, make decisions, and apply logic to situations. When we’re stressed, however, the prefrontal cortex can become less active, and our emotional responses can take over.
- The Nervous System: Emotions also have a physical component. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for activating our “fight, flight, or freeze” responses in times of stress. This system triggers changes in our body such as increased heart rate, shallow breathing, or muscle tension. When we experience positive emotions like relaxation or joy, this system shifts into a state of calmness, allowing our bodies to relax.
In short, emotions are not just “in our heads”—they’re deeplyconnected to how our bodies respond to the world around us. This mind-body connection is essential to understanding and working through difficult emotions in therapy.
Why Do Emotions Sometimes Feel So Intense or Confusing?
Many people find emotions confusing or overwhelming because they often arise automatically, without conscious thought. It’s easy to feel like emotions take over, or that we have no control over them.
Emotions can also be influenced by past experiences, which can shape how we respond to current situations. For example, someone who has experienced trauma or loss might have stronger emotional reactions to situations that trigger memories of those events. Similarly, if you’ve grown up in an environment where certain emotions weren’t expressed or were invalidated, you might find it difficult to identify or communicate your feelings as an adult.
This is where therapy can be especially helpful: by exploring the root causes of your emotional patterns, you can learn to understandand regulate them more effectively.
The Role of Thoughts in Shaping Emotions
While emotions themselves are natural, our thoughtshave a significant impact on how we experience and react to them. In fact, how we interpret an event or situation can influence the emotional response we have. For instance:
- If you perceive a situation as a threat, your body will respond with fear or anxiety (even if there’s no real danger).
- If you see something as positive or exciting, you may experience joy or excitement.
- If you interpret something as unfair or unjust, you may feel anger or frustration.
This interplay between thoughts and emotions is often explored in therapy, especially in cognitive-behavioral approaches. By identifying and challenging negative thought patterns, you can begin to shift your emotional responses and reactions to situations.
The Importance of Emotional Awareness and Expression
One of the keys to emotional well-being is becoming more awareof your emotions and how they manifest in your body and mind. Emotional awareness helps you identify when something feels off and gives you the tools to explore why you’re feeling the way you do. Being aware of your emotions also allows you to take steps toward emotional regulation—the process of managing or changing your emotional responses.
Here are a few tips for becoming more emotionally aware:
- Tune into your body: Emotions often show up physically first. Pay attention to tension in your muscles, tightness in your chest, or changes in your breathing.
- Label your emotions: Putting a name to what you’re feeling (e.g., “I feel angry,” “I feel anxious,” or “I feel sad”) can help you gain clarity. Sometimes we experience a mix of emotions, so try to identify the primary feeling and work from there.
- Sit with your emotions: Instead of avoiding or suppressing them, try to sit with your feelings. Acknowledge them without judgment. Let them come and go. Emotions are like waves—they often pass if we allow ourselves to experience them fully.
- Express your emotions: Talking to someone you trust, writing in a journal, or even engaging in physical activities like movement or art can help release pent-up emotions. Therapy provides a safe space to express and explore your emotions in a supportive, non-judgmental environment.
How Therapy Can Help You Understand and Manage Your Emotions
In therapy, we explore the underlying causes of your emotions—whether they stem from past experiences, current stressors, or thought patterns. The goal isn’t to eliminate emotions but to understand them and learn how to respond to them in healthy, constructive ways.
Therapy can help you:
- Identify emotional triggers: Understand what causes you to feel overwhelmed, angry, sad, or anxious, and work through those triggers.
- Regulate emotions: Learn tools to manage and cope with intense emotions, such as mindfulness, relaxation techniques, and grounding exercises.
- Challenge unhelpful thoughts: By recognizing the connection between your thoughts and feelings, you can change negative or irrational thought patterns and create a more balanced emotional experience.
- Heal emotional wounds: Unresolved trauma or difficult experiences can manifest in emotional distress. Therapy can help you process and heal these emotional wounds, leading to a greater sense of peace and emotional stability.
Conclusion: Emotions Are a Natural Part of Being Human
Emotions are a powerful part of being human, and understanding them can be the first step toward emotional well-being. They offer us valuable information about ourselves and the world, helping us navigate our relationships, decisions, and life experiences. By learning how emotions work, you can create a healthier relationship with your feelings and develop tools to manage them more effectively.
If you’re ready to start exploring your emotions in therapy, I’d be happy to help. Together, we can work through your feelings, identify any patterns that may be holding you back, and help you find ways to move forward with greater emotional balance and clarity.
Healing starts with understanding—and I’m here to support you every step of the way.